Understanding Agentic AI: The Future of Autonomous Decision-Making
Understanding Agentic AI: The Future of Autonomous Decision-Making
AI continues to evolve, with advancements steering the technology towards greater independence and adaptability. At the forefront of this evolution is "Agentic AI", a branch of AI that exhibits goal-oriented, autonomous decision-making capabilities. Unlike traditional AI systems that require detailed instructions, agentic AI can independently plan, adapt, and execute tasks aligned with pre-defined objectives.
This breakthrough has far-reaching implications for industries and society, promising efficiency and innovation but also raising ethical and safety concerns. This article delves into the concept of Agentic AI, its current applications, and the considerations for its responsible development.
Get in Touch!

Main section
Quick facts
/
Agentic AI refers to systems that demonstrate goal-oriented and autonomous behavior
/
AI Agents focus on achieving objectives without constant human oversight
/
Applications range from healthcare and finance to robotics and human resource management
/
Ethical challenges include accountability, safety, bias and transparency
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI represents a paradigm shift in artificial intelligence. The term "agentic" refers to the quality of being an agent—a system capable of acting autonomously in pursuit of a goal. Unlike rule-based or supervised machine learning models, agentic AI systems operate with a degree of independence that allows them to assess situations, make decisions, and execute actions without continuous human intervention.
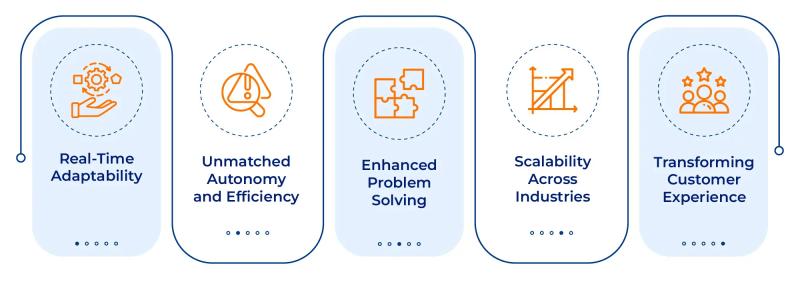
At its core, Agentic AI integrates 3 key attributes:
- Autonomy: The system can make decisions independently.
- Goal Orientation: It prioritizes achieving specific objectives.
- Adaptability: It adjusts to changing circumstances or environments dynamically. It also learns from outcomes to refine future actions.
These capabilities are achieved through advanced algorithms, reinforcement learning, and complex decision trees that simulate human-like reasoning. A classic example is autonomous vehicles, which must navigate unpredictable environments while adhering to safety and efficiency goals.
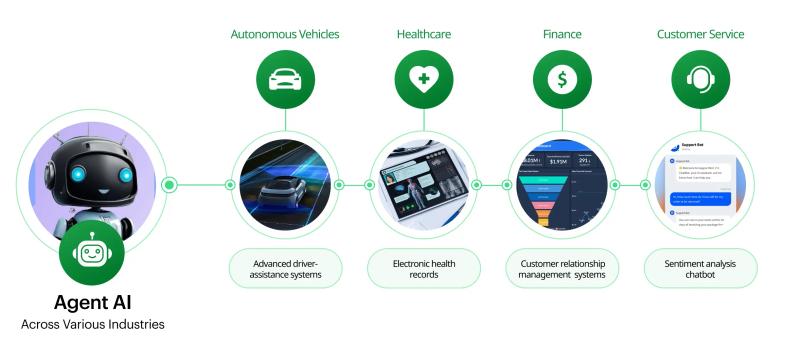
Applications of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is also closely linked to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a cutting-edge approach that combines generative AI with real-time data retrieval. In RAG, agentic systems autonomously fetch relevant external information to enhance their decision-making capabilities and generate contextually accurate outputs (less hallucination).
This concept was explored in detail in a previous article about RAG and Private AI, where the focus was on how RAG ensures data privacy and real-time accuracy in sensitive environments. This synergy enables applications in knowledge-intensive fields like research, customer service, and legal analysis, where real-time updates are critical.
Agentic AI has a growing presence in various fields, demonstrating its transformative potential:
- Healthcare: AI agents assist in diagnostics, personalized treatment planning, and even performing surgeries. These systems can analyze vast datasets, identify patterns, and make recommendations tailored to individual patients.
- Finance: Algorithmic trading platforms employ agentic AI to analyze market trends, predict outcomes, and execute trades autonomously, optimizing portfolio performance in real-time.
- Robotics: Robots equipped with agentic AI are used in manufacturing, logistics, and even household tasks. They adapt to changing conditions and optimize their functions without direct supervision.
- Human Resources (HR): Agentic AI is transforming HR by automating candidate screening, conducting preliminary interviews through AI-driven chatbots, and even providing personalized employee training programs. These systems assess qualifications and predict cultural fit, saving time and improving hiring outcomes.
Ethical and Practical Challenges, and the link with the EU AI Act
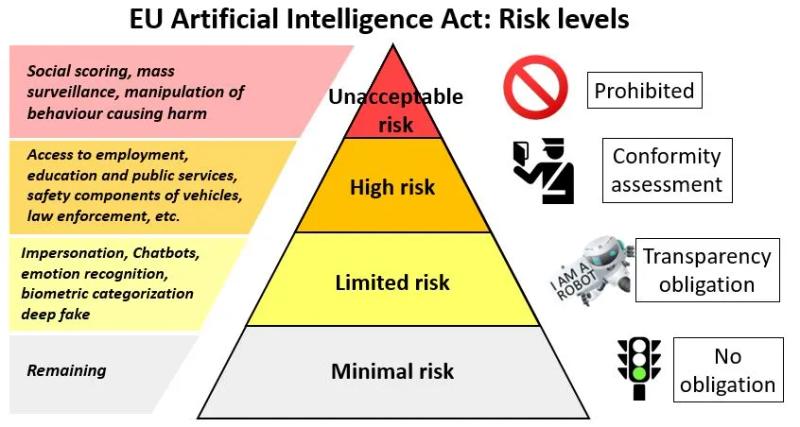
While the potential of Agentic AI is vast, it also brings significant challenges, many of which are directly addressed by the European Union's AI Act. This regulation aims to establish a legal framework to govern the safe and ethical use of artificial intelligence, including agentic systems. By emphasizing requirements for transparency, accountability, and bias mitigation, the AI Act provides guidelines that align closely with addressing concerns over the safety, predictability, and trustworthiness of autonomous AI systems.
- Accountability: Determining responsibility for the actions of autonomous systems can be complex. The EU AI Act emphasizes the need for clearly defined liability frameworks to ensure that both developers and operators are held accountable for the outcomes of AI systems. For instance, Article 22 of the Act mandates that entities deploying high-risk AI maintain detailed records of decision-making processes, enabling traceability and accountability.
- Safety: Ensuring these systems act reliably and predictably under all circumstances is critical. The EU AI Act directly addresses this by mandating rigorous testing and risk management protocols for high-risk AI systems. For example, Article 9 of the Act outlines stringent safety requirements, ensuring that systems undergo pre-deployment evaluation and continuous monitoring to mitigate risks and enhance reliability.
- Transparency: Understanding the decision-making processes of highly autonomous systems is essential for trust. The EU AI Act addresses this by requiring clear documentation and explainability of AI systems. Article 13 mandates that users of high-risk AI systems be provided with concise and transparent information about their functionality, enabling stakeholders to understand and evaluate how decisions are made.
- Bias: Mitigating bias in agentic AI requires rigorous training and oversight. The EU AI Act specifically addresses this issue in Article 10, which mandates the use of high-quality, representative training datasets and regular audits to identify and correct biases. These measures aim to prevent discriminatory outcomes and ensure fairness in AI-driven decisions.
Regulatory frameworks and industry standards are still evolving to address these challenges. Developers and policymakers must collaborate to ensure that the benefits of Agentic AI outweigh the risks.
Bottom section
The Road Ahead for Agentic AI: Resources for Further Research
Agentic AI is poised to redefine the boundaries of what AI can achieve. As industries adopt these advanced systems, they must balance innovation with ethical considerations to foster responsible growth.
The future of Agentic AI will depend on multidisciplinary efforts to refine its algorithms, improve its adaptability, and ensure its decisions align with human values.
For further exploration, researchers and enthusiasts can delve into recent advancements in reinforcement learning, ethical AI frameworks, and autonomous systems development.
Here are some of the best resources for learning and researching the interesting field of Agentic AI:
- Navigating the AI Frontier: A Primer on the Evolution and Impact of AI Agents: This white paper by the World Economic Forum explores the development of AI agents and highlights how thesecan enhance efficiency across sectors including healthcare, education and finance
- Challenges in human-agent communication: New Microsoft research explores 12 challenges for modern AI agents with concrete examples.
- AI Act Explorer: A great searchable overview of the articles, annexes and recitals
- Agentic AI - The new frontier in AI, an executive playbook by PwC
- State of AI Agents: a huge survey by LangChain on how AI agents are being used (or not) today
- AI Agents: a New Architecture for Enterprise Automation (Menlo Ventures)
- The Agentic Web (James Detweiler Eric Flaningam of Felicis)
- AI is about to completely change how you use computers and upend the software industry (Bill Gates' note on AI agents back in 2023)
- Large Language Model Agents (Stanford Univ. online course, fall 2024)
- Building Effective Agents (Anthropic)
- Agents Are Not Enough: we also need Sims and Assistants (Microsoft & UWash)
- 30+ Pre-Built Agents and Agent Templates from Microsoft for M365, D365, Copilot Studio, ...
By understanding and shaping the trajectory of Agentic AI, society can harness its full potential of AI and automation, while minimizing risks.
Make sure to follow Cyber3Lab on LinkedIn, ensuring a future where technology serves humanity responsibly.
Contributors
Authors
/
Patrick Van Renterghem, AI, CyberSecurity, Web3, Immersive Tech, Quantum, ... Community Builder & LLL Coordinator
Want to know more about our team?
Visit the team page
Last updated on: 3/24/2025
/
More stuff to read




